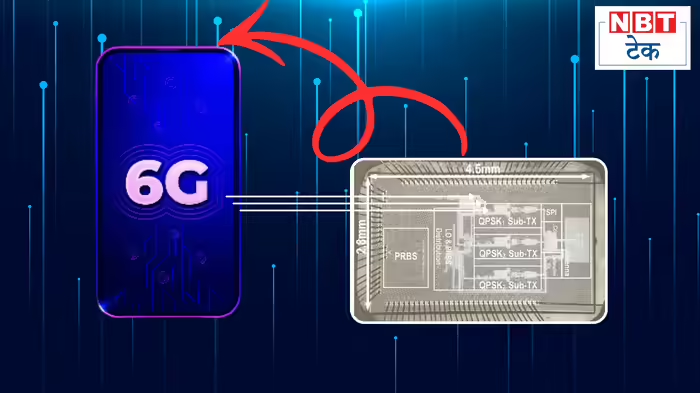
American engineers have achieved a major milestone in wireless technology, developing a silicon chip capable of transmitting data at speeds comparable to fiber optic cables. This innovation could be a game-changer for 6G networks and future high-speed communication needs.
About the Achievement
The breakthrough comes from a team of electrical engineers at UC Irvine, California, led by Professor Pem Hedari. Since 2020, the team has been working on designing a wireless chip that can handle ultra-high-speed data transmission efficiently. Unlike existing wireless chips, which struggle with high-speed data and consume large amounts of energy, this new chip transmits data rapidly and with minimal power consumption, opening doors for advanced transmission protocols in the future.
How It Works
Currently, high-speed data is primarily transmitted using fiber optic cables. The new wireless chip allows comparable speeds without physical cables, enabling data to be sent and received from anywhere in the world at unprecedented speeds.
Existing wireless transmitters rely on digital-to-analog converters (DACs), which limit speed and increase energy usage. For 6G, transmitters need to operate at frequencies above 100 GHz, far beyond current DAC-based systems. Hedari’s team eliminated the DAC block, generating signals directly in the radio-frequency spectrum. This enables the chip to transfer large volumes of data rapidly without overheating, while maintaining energy efficiency.
Preparing for 6G Devices
The engineers also developed a smart receiver compatible with devices like smartphones, ensuring that future 6G-enabled devices can receive ultra-fast data seamlessly. The chip’s low power consumption and scalable design make it suitable for mass production and widespread adoption.
Significance
This breakthrough represents a critical step toward realizing wireless data transmission speeds equivalent to fiber optics, paving the way for 6G networks, ultra-fast mobile connectivity, and future applications that demand extremely high bandwidth.
With this innovation, the era of truly fiber-like wireless internet could soon become a reality, transforming communication, cloud computing, and real-time data sharing across the globe.
Discover more from SD NEWS agency
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
