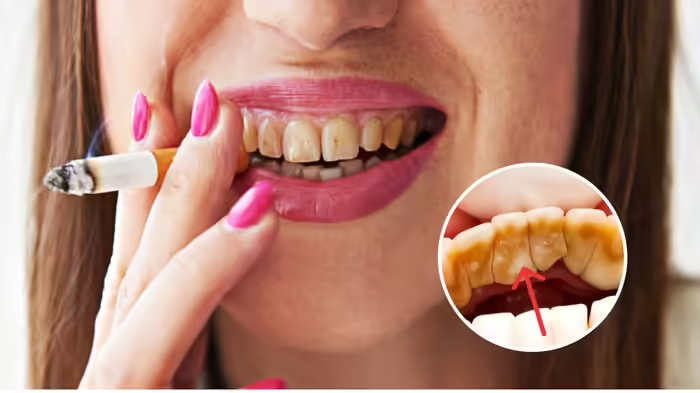
Periodontitis is a serious gum disease that does not just damage the teeth and jaw, but can also trigger several life-threatening health conditions. Medical experts warn that people already suffering from heart disease, diabetes, or respiratory disorders should never ignore gum problems and must undergo regular dental check-ups.
Bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and loose teeth are common oral problems that many people overlook. Among these, periodontitis is a chronic and severe condition of the gums that progresses slowly but can cause irreversible damage. It is not limited to the mouth alone; the inflammation associated with this disease can affect the entire body.
What is Periodontitis?
According to Dr. Tanu Gupta, Senior Consultant – Dental Sciences, Shardacare Healthcity, periodontitis occurs when plaque and harmful bacteria accumulate around the teeth and gums. If left untreated, the infection spreads deeper, damaging the supporting tissues and jawbone.
As the infection progresses, gums begin to separate from the teeth, forming deep pockets where bacteria thrive. These bacteria and the toxic substances they produce can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Doctors emphasize that periodontitis is not merely a dental issue but a systemic health concern.
Serious Health Risks Linked to Periodontitis
Heart Disease:
People with severe gum disease are at a higher risk of heart attack and stroke. Studies have found oral bacteria in the arteries, which can increase inflammation and contribute to blocked blood vessels.
Diabetes:
The relationship between diabetes and gum disease works both ways. Poorly controlled diabetes weakens the gums, while gum inflammation makes blood sugar levels harder to manage, increasing the risk of kidney, eye, and nerve damage.
Respiratory Diseases:
Bacteria from infected gums can be inhaled into the lungs, raising the risk of pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), especially in elderly individuals and those with low immunity.
Pregnancy Complications:
Pregnant women with gum disease face a higher risk of premature delivery and low birth-weight babies. Inflammatory substances may interfere with fetal development.
Apart from these, periodontitis has also been linked to arthritis, kidney disease, and even memory-related disorders.
Why is This Disease So Dangerous?
The biggest danger of periodontitis lies in its silent progression. Symptoms such as bleeding while brushing, swollen gums, constant bad breath, receding gums, or slightly loose teeth are often ignored. By the time pain becomes severe or teeth start loosening significantly, substantial damage has already occurred.
Prevention and Treatment
Periodontitis can largely be prevented, and early treatment can stop its progression. Even in patients already affected, timely care can reduce complications and lower the risk of related systemic diseases.
Dentists recommend these 5 essential steps:
- Brush twice daily using fluoride toothpaste
- Clean between teeth with floss or interdental cleaners
- Visit a dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleaning
- Quit smoking, keep diabetes under control, reduce stress, and maintain a balanced diet
- If required, undergo early treatments such as deep cleaning, medication, or surgical procedures
Disclaimer:
This article is for general information only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice or treatment. Readers are advised to consult a qualified doctor or dentist for personalized guidance. The publication does not take responsibility for the accuracy or outcomes of the information provided.
Discover more from SD NEWS agency
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
