Gas-related stomach discomfort is common, but doctors often warn against ignoring it, as it can sometimes indicate serious heart problems. Chest pain from a cardiac arrest or heart attack can mimic the sensation of gas buildup. A striking case from Gurugram illustrates this danger.
A 41-year-old patient arrived at the Fortis Memorial Research Institute emergency department complaining of mild gas-related discomfort. Initially, the issue seemed minor, but his condition quickly deteriorated, prompting urgent medical tests. The patient was diagnosed with cardiac arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, and a complete blockage of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery.
Heart Test Saves the Day
The patient was initially hesitant to undergo an ECG, the test that monitors the heart’s electrical activity. However, this very test revealed the classic “shock fin” pattern, a life-saving clue for the doctors.
Dr. Mohammad Nadeem, Head of Emergency Medicine at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram, said, “A patient with minor discomfort rapidly progressed to cardiac arrest. Surviving after multiple resuscitation attempts, repeated electric shocks, and prolonged cardiac arrest is extremely rare. This case serves as a reminder not to ignore chest discomfort.”
Understanding the ‘Shock Fin’ Pattern
The shock fin pattern appears on an ECG when a major artery supplying blood to the heart is completely blocked. Immediate emergency angiography confirmed a 100% blockage in the proximal left anterior descending artery.
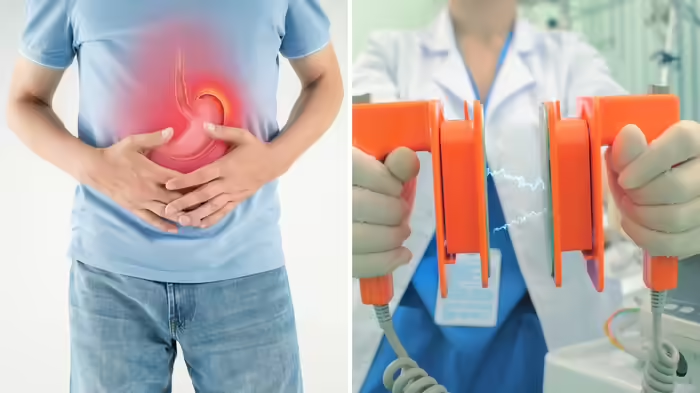
23 Electric Shocks to Stabilize the Heart
The patient received 23 electric shocks using advanced sequential defibrillation, along with high-quality CPR, airway stabilization, and heart medications. Once stabilized, he was taken to the cath lab for an emergency percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), restoring blood flow to the heart.
What is Percutaneous Coronary Intervention?
Percutaneous coronary intervention is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked coronary arteries. Previously referred to as angioplasty with stenting or simply angioplasty, PCI restores blood supply and prevents further cardiac damage.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only. NBT does not guarantee its accuracy or efficacy. It should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified doctor for guidance.
Discover more from SD NEWS agency
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
